“There is nothing radical in what we’re discussing,” journalist and climate change activist Bill McKibben said before a crowd of nearly 1,000 at the University of California Los Angeles last night. “The radicals work for the oil companies.”
Taken on its own, a statement like that would likely sound hyperbolic to most Americans—fodder for a sound bite on Fox News. Anyone who saw McKibben’s lecture in full, however, would know he was not exaggerating.
McKibben was in Los Angeles as part of his nationwide “Do the Math” tour. Based on a recent article of his in Rolling Stone, (“The one with Justin Bieber on the cover,” McKibben joked) the event is essentially a lecture circuit based on a single premise: climate change is simple math—and the numbers do not look good. If immediate action isn’t taken by global leaders: “It’s game-over for the planet.”
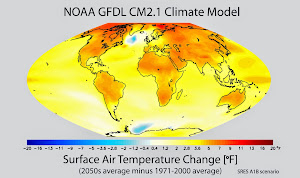
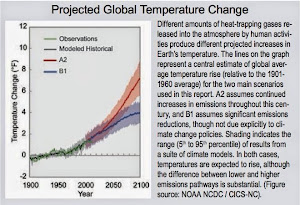
The math, McKibben explained, works like this. Global leaders recently came to an international agreement based on the scientific understanding that a global temperature raise of 2°C would have “catastrophic” consequences for the future of humanity. In order to raise global temperatures to this catastrophic threshold, the world would have to release 565 gigatons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Here’s the problem: Fossil fuel companies currently have 2,795 gigatons of carbon dioxide in their fuel reserves—and their business model depends on that fuel being sold and burned. At current rates of consumption, the world will have blown through its 565-gigaton threshold in 16 years.
To prevent the end of the world as we know it, it will require no less than the death of the most profitable industry in the history of humankind.
“As of tonight,” McKibben said, “we’re going after the fossil fuel industry.”
Obviously no easy task. The oil industry commands annual profits of $137 billion and the political power to match. As McKibben noted, “Oil companies follow the laws because they get to write them.”
However, there are some numbers on McKibben’s side. Recent polling data shows 74 percent of Americans now believe in climate change, and 68 percent view it as dangerous. The problem environmental activists are facing is in converting those favorable polling numbers into grassroots action.
Enter “Do the Math.”
Using McKibben’s popularity as an author, organizers are turning what would otherwise be a lecture circuit into a political machine. Before rolling into town, Do the Math smartly organizes with local environmental groups. Prior to McKibben’s lecture, these groups are allowed to take the stage and talk about local initiatives that need fighting. Contact information is gathered to keep the audience updated on those efforts. Instead of simply listening to McKibben, as they perhaps intended, the audience has suddenly become part of their local environmental movement.
It’s a smart strategy, and an essential one—because the problem of climate change is almost exclusively a political in nature. Between renewable energy and more efficient engineering, the technology already exists to stave off catastrophic global warming. Though its application is lagging in the United States, it is being employed on a mass scale in other countries. In socially-stratified China, with its billion-plus population and tremendous wealth inequalities, 25 percent of the country still manages to use solar arrays to heat its water. Germany—Europe’s economic powerhouse—in less than a decade, has managed to get upwards of half of its energy from sustainable sources.
The same can happen here in America—provided we have the will to make it happen. McKibben says the key to realizing that goal is to battle the lifeblood of the fossil fuel industry—its bottom line.
To start, he’s calling for an immediate global divestment from fossil fuel companies. “We’re asking that people who believe in the problem of climate change to stop profiting from it. Just like with divestment movement in South Africa over apartheid, we need to eliminate the oil companies veneer of respectability.”
In conjunction with the divestment regimen, continued protests against unsustainable energy projects will also be crucial. McKibben will be in Washington, D.C. on November 18 to lead a mass rally against climate change and the Keystone Pipeline. “We can no longer just assume that President Obama is going to do everything he promised during his campaign. We need to push him.”
“I don’t know if we’re going to win. But I do know we’re going to fight.” More